
Key Words:
SQL Database, Relational Database Design & Management, ER Diagram, Healthcare Data
Tools:
MySQL, MySQL Workbench, Lucidchart
Project Link:
Project Overview
Coming from a psychology background, I understand that many therapists face challenges in managing data when starting their own clinics. Without expertise in data management, they often worry about data security, patient privacy, and potential breaches when relying on external services. To address these concerns, I designed a clinic database that is both easy to manage and comprehensive in functionality.
This database securely stores and manages various types of clinical information, including patient records, diagnoses, therapy sessions, psychological assessments, medications, and attendance. It allows both patients and staff to efficiently access relevant information. Patients can check their appointments, prescribed treatments, and therapy progress, while staff can manage scheduling, update patient records, log assessments, and review treatment histories.
Approach & Design
I started by sketching an initial draft on a whiteboard, outlining the overall direction and identifying key tasks the database needed to support. This helped determine the essential tables required for managing clinical data.
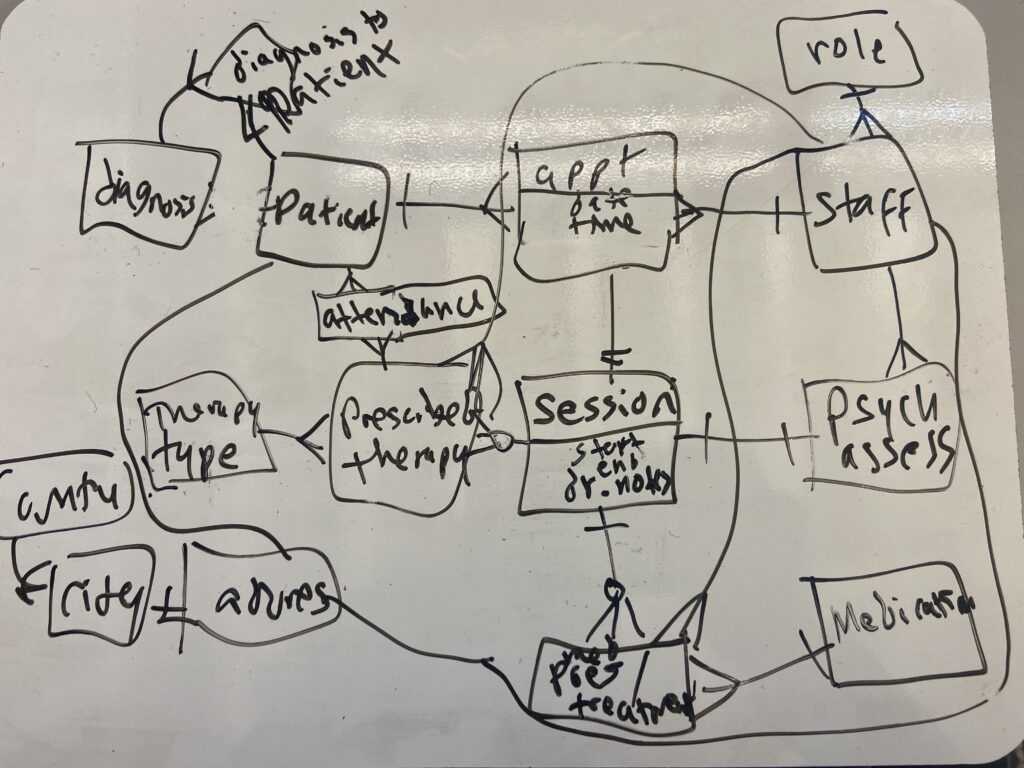
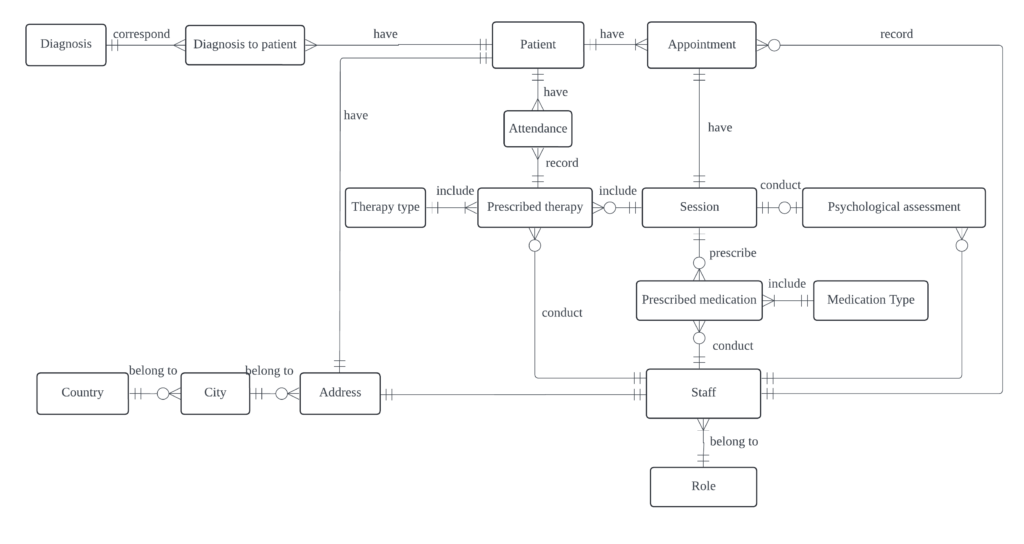
After defining the initial tables, I used Lucidchart to visualize the conceptual database structure and establish relationships between entities. Since the database focuses on specific mental health patients, such as those with ADHD, rather than covering all types of illnesses, I structured patient visits around three possible actions: undergoing psychological assessment, participating in psychotherapy, or receiving medication treatment.
Psychotherapy and medication treatment are further categorized into various types, such as group therapy, individual attention training, and problem-solving training for psychotherapy, and long-acting and short-acting medications for medication treatment. This necessitated the creation of additional tables for classification.
Furthermore, clinic staff hold different roles—such as physicians, psychologists, and administrative staff—each with distinct responsibilities, requiring role-based task management. Additionally, patient and staff records include address information, necessitating city and country tables for proper organization. Throughout this process, I identified the need for intermediary tables to enhance data connectivity and ensure referential integrity.
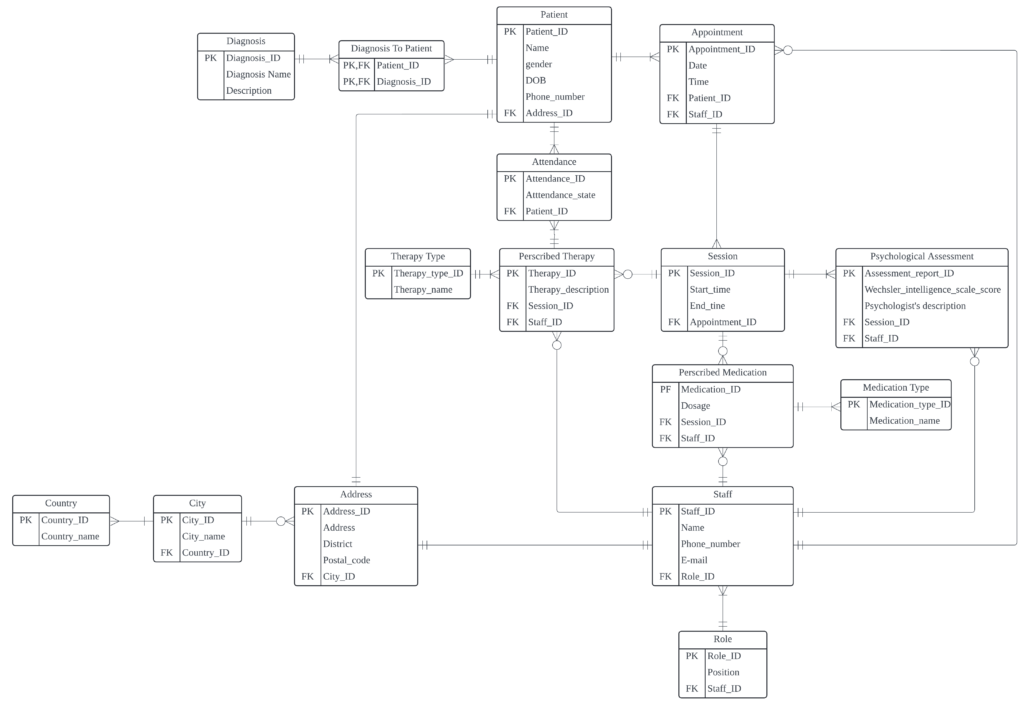
Once the conceptual structure was complete, I began defining the internal attributes of each table and assigned primary keys (PK) and foreign keys (FK) to establish clear relationships and enforce data consistency.
Implementation
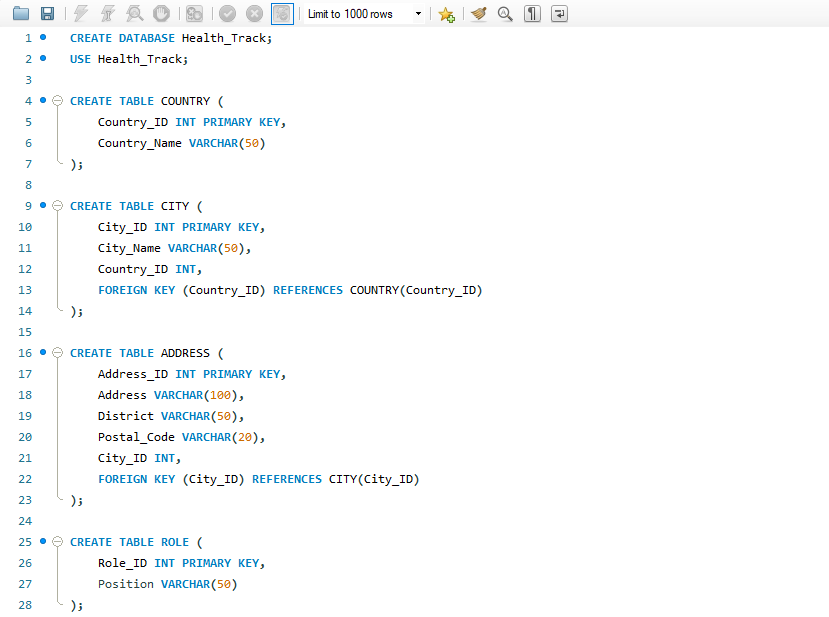
With the database structure finalized, I implemented it in MySQL Workbench, creating tables, defining constraints, and setting up relationships based on the planned schema. The process involved writing SQL scripts to establish table structures, assign primary keys (PK) and foreign keys (FK), and enforce data integrity with constraints such as NOT NULL, UNIQUE, and CHECK.
The screenshot below shows the initial setup of key tables, including Country, City, Address, and Role, along with their relationships.
To test the database functionality and ensure smooth execution of tasks, I inserted 10 sample records into each table. These records simulate real-world data, allowing me to verify relationships between tables, validate constraints, and test queries for retrieving patient, staff, and treatment information.
During the testing stage, I encountered some errors in placing foreign keys (FKs). To ensure proper data relationships, I corrected these errors, particularly in “Many” side relationships, where foreign keys needed to be appropriately positioned. Additionally, I added start date and end date fields to the “Diagnosis to Patient” table, allowing patients to track the timeline of their diagnoses.
Furthermore, I refined several queries to align with system requirements and introduced new queries for TRANSACTION and TRIGGER to enhance database functionality and maintain data integrity.

Final Deliverable
To finalize the database design, I used MySQL Workbench’s built-in feature to regenerate the ER diagram, ensuring that all relationships and structures were correctly implemented.
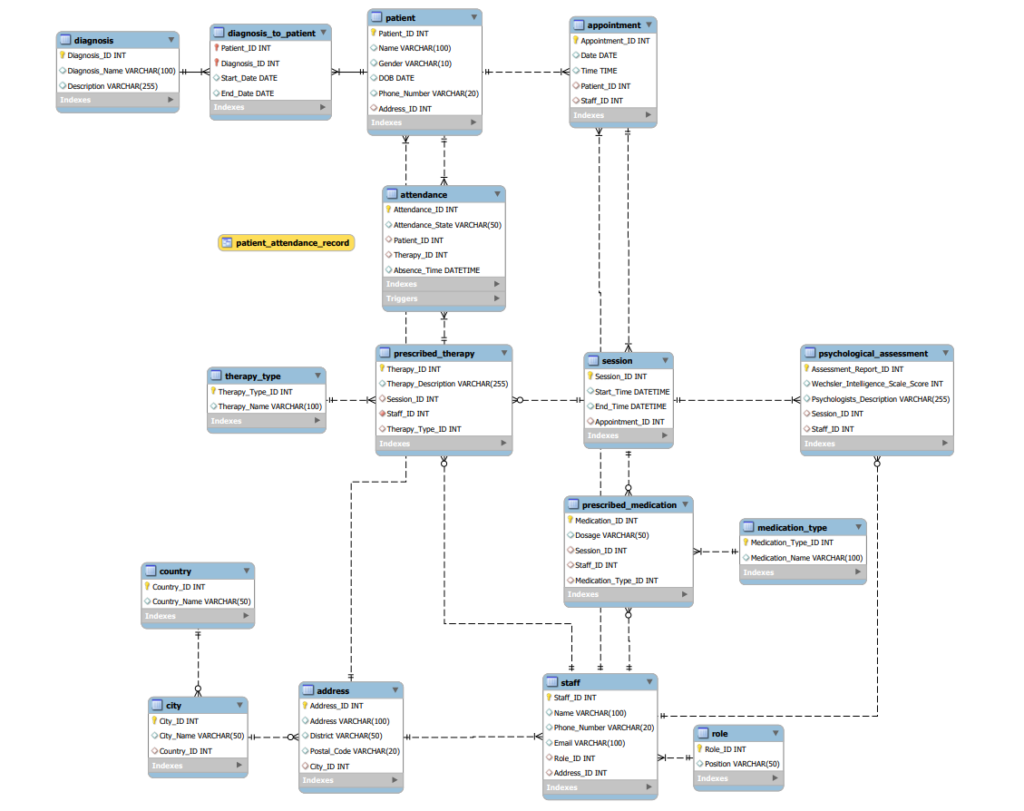
The complete SQL script for the database, including table creation, constraints, and sample queries, is available on GitHub at the following link: here
